Sodium Ion vs. Lithium-Ion batteries; both are sustainable and efficient energy storage options. Regardless, batteries play an important role in powering up our lives. Batteries provide renewable energy from smartphones to laptops to electric vehicles to our portable items.
Lithium-ion batteries have dominated the market with their high energy density and efficiency. These batteries are the centre of attention when it comes to technology. If you look at the periodic table, the element below Lithium can replace it.
Yes, we are talking about Sodium!
As per the technological advancements, sodium-ion batteries can achieve similar performance compared to Lithium-Ion batteries. The abundance and affordability of Sodium can make it more of a substitute. The rising demand for batteries has skyrocketed the prices of Lithium.
As per Jason Zhang, known to be a pioneer in battery research, “Sodium has an almost unlimited supply.” In this blog, we will dive deeper into understanding the key differences between Sodium and Lithium-Ion batteries, their functionalities and the potential of Sodium Ion batteries to replace Lithium-Ion batteries.
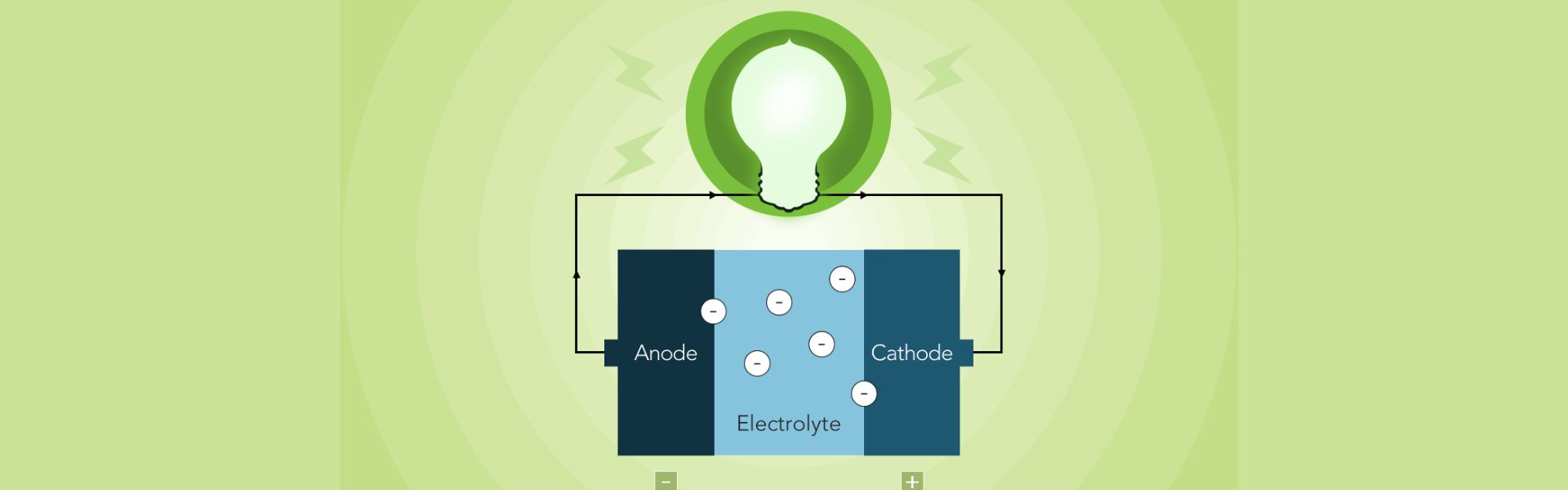
Basics! Both Lithium and Sodium batteries are rechargeable. They can undergo multiple charging and discharging cycles. The batteries’ function is the same; ions move between positive and negative electrodes through an electrolyte, releasing and storing energy.
In a Lithium-Ion battery, the Ion moves from a positive to a negative electrode, From lithium cobalt oxide to graphite, during the discharge cycle and vice versa during the charge cycle.
Sodium Ion batteries work on the same concept. But, Sodium Ion batteries use sodium-based electrolytes that enable the flow of sodium ions.
What is Common Between Lithium and Sodium Batteries:
Chemically, Sodium and Lithium are similar, and the batteries are also constructed similarly. The movement of Ions is also similar during the charge and discharge cycles.
- Both the batteries are rechargeable, with multiple charge and recharge cycles.
- The batteries are of the same nature, relying on electrochemical reactions to store and release energy facilitated by the movement of ions within the battery.
What is the Difference Between Lithium and Sodium Batteries:
Lithium Ion and Sodium Ion batteries are two types of rechargeable batteries. Both types work with electrochemical reactions. They do have similarities, but the two types have several significant differences.
Chemistry of Electrodes:
Lithium-Ion batteries are equipped with lithium compounds, a positive electrode (cathode), typically lithium cobalt oxide, manganese oxide, or lithium iron phosphate. The negative electrode (anode) is made of graphite, allowing a reversible extraction and insertion of lithium ions during charge and discharge cycles.
Sodium Ion batteries have sodium-based compounds for both negative and positive electrodes. The common electrodes are sodium cobalt oxide and sodium iron phosphate. However, hard carbon and other sodium ion storage materials are used on the negative side.
Energy Density:
The energy density of Lifepo4 batteries is relatively high compared to Sodium-Ion batteries. Meaning they can store more energy in a smaller and lighter package. Hence, Lithium-Ion batteries are more suitable for portable devices and electronic vehicles based on the energy density factor. The energy density of a Lithium-Ion battery is about 180Wh/kg.
On the other hand, Sodium Ion batteries have a low energy density. Hence, not suitable for devices that require high-performance energy storage. The energy density of a Sodium Ion battery is about 100-150 Wh/kg
Performance and Efficiency:
Lithium-ion batteries benefit better in performance as compared to Sodium-Ion batteries. They have a high discharge and charge efficiency and consume less energy during the cycles. Not to mention, Lithium-Ion batteries have a longer life span and allow multiple charge/discharge cycles.
Sodium Ion batteries have a low-efficiency level and a shorter life cycle in comparison. Certain devices are unreliable as they only hold a few charge/discharge cycles.
Cost and Availability:
One of the significant drawbacks of Lithium-Ion batteries is the cost and scarcity. The extraction of Lithium is challenging, and the mining of the element is expensive, which leads to higher battery costs.
Sodium is widely available and distributed globally, making it a cheaper alternative to Lithium-Ion batteries. The abundance of the sodium element leads to lower production costs.
Moreover, Lithium is not widely available hence the hike in prices. Whereas, Sodium is available and can be extracted from seawater as well. Lithium is less environmentally friendly as compared to Sodium. Also, Sodium has no risk of thermal runaway; Lithium can cause it to operate in higher temperatures.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Lithium vs Sodium Batteries:

Lithium-Ion Batteries Advantages:
- They have a high energy density.
- The lifespan is longer and has efficient cycling performance.
- The charge/discharge cycles are around 2500-3000.
- The self-discharge rate is 3% per month.
- They are lighter in weight.
Sodium-Ion Batteries Advantages:
- They are widely available.
- The extraction cost is cheaper and can be extracted from seawater.
- Sodium batteries are easier to recycle.
- They can operate in a higher temperature range.
- There is no risk of thermal runaway.
Lithium-Ion Batteries Disadvantages:
- The extraction cost is expensive.
- It is not widely available.
Sodium-Ion Batteries Disadvantages:
- The energy density is low.
- They are bulkier in weight.
- The charge/discharge cycles are roughly around 1000-1500
Why Are Sodium Batteries Not Used Extensively?
Sodium Ion has similar properties as Lithium Ion and can be used as an alternative to Lithium-Ion batteries. However, they are used sparingly due to some challenges. The lower energy density and efficiency of sodium-ion batteries are incapable, making them less suitable for applications that demand compact and high-performance energy storage.
The technology for Sodium-Ion batteries is still in the early stages of the development process; and requires more research to improve its performance.
Can Sodium-ion Batteries Replace Lithium-ion Batteries?
Sodium Ion batteries have similarities with Lithium Ion batteries, but they cannot currently replace them because of low energy density issues and low efficiency. Also, Sodium Ion batteries’ life cycle is short-lived, making them less suitable for high–performing devices.
It’s a Wrap:
Different types of Lithium-Ion batteries have revolutionized the world of electronics and car batteries. However, the element is not widely available; there is scarcity, and the extraction process is also expensive, which makes it even more costly. Hence, alternatives are explored for high-performing applications. Sodium-ion batteries have similar properties and can be used as a substitute, but they can not replace Lithium-Ion batteries. There needs to be more efficiency between the two batteries.
FAQ’s:
What are lithium-ion batteries, and how do they work?
Lithium-ion batteries are renewable energy storage devices that utilise lithium ions to transfer the charge between negative and positive electrodes. The ions move from positive to negative during the discharge phase and vice versa during the charge phase.
What is sodium-ion batteries, and how do they differ from lithium-ion batteries?
Sodium Ion batteries are also rechargeable. They are equipped with sodium Ion which helps store and release energy. Sodium Ion batteries are short-lived and have a low energy density.
Which battery type has a higher energy density?
Lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density and can store more energy in a compact and light device. The energy density of Lithium Ion is approximately 180WH/kg.
What are the advantages of using lithium-ion batteries?
Lithium-Ion batteries have a high energy density and it also has a longer life span. Moreover, the charge/discharge cycles are around 2500-300; and have a well-established manufacturing process.